Welded steel pipes are manufactured by forming steel plates or coils into a cylindrical shape and joining the edges through various welding techniques. These pipes are classified based on their production methods, with common types including Electric Resistance Welding (ERW), Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), and High-Frequency Induction Welding (HFIW). Available in diameters ranging from 10mm to 2,000mm and wall thicknesses from 1mm to 25mm, welded pipes meet international standards such as API 5L, ASTM A53, and EN 10219.
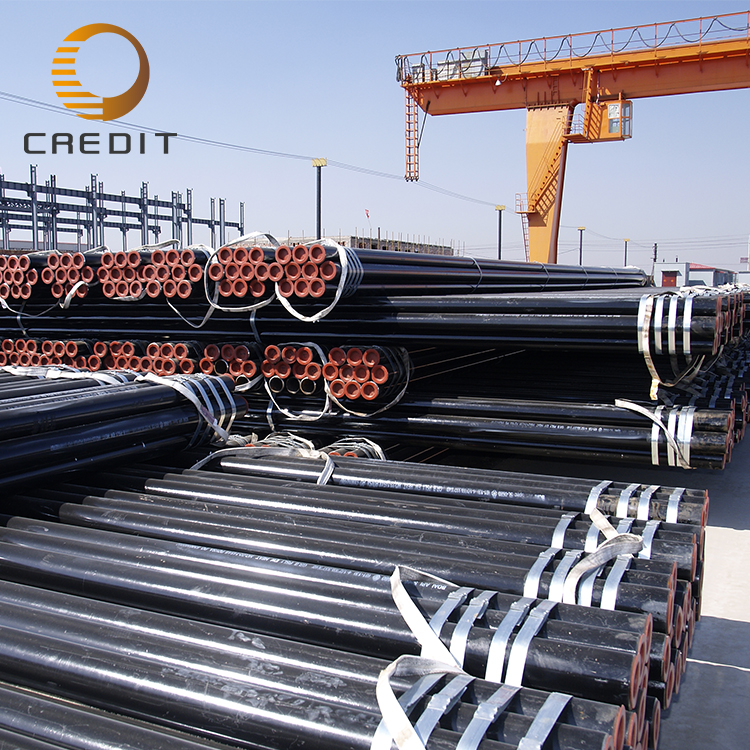

These pipes find extensive applications in water and gas distribution systems, structural projects, fencing, and low-to-medium pressure pipelines. Their advantages include cost-effectiveness in production, high manufacturing efficiency, and the capability to produce large diameters. The consistent quality and reliability of welded pipes make them suitable for various industrial uses where high performance and durability are required.
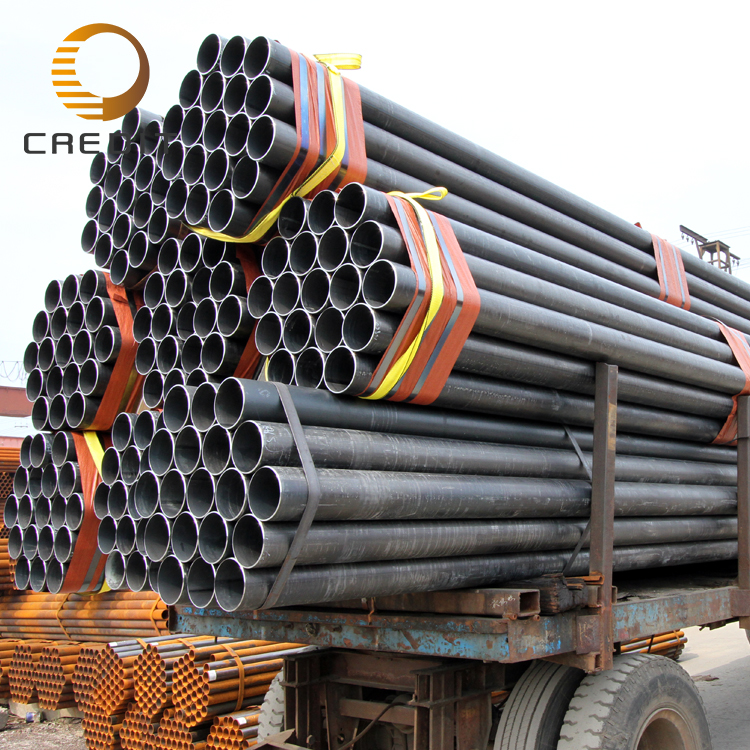

The global market for welded steel pipes is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging economies. Future trends indicate a shift towards automated welding technologies and the adoption of high-strength steel grades to enhance product performance and sustainability. The growing demand for efficient fluid transportation systems and construction materials is expected to further boost market prospects.
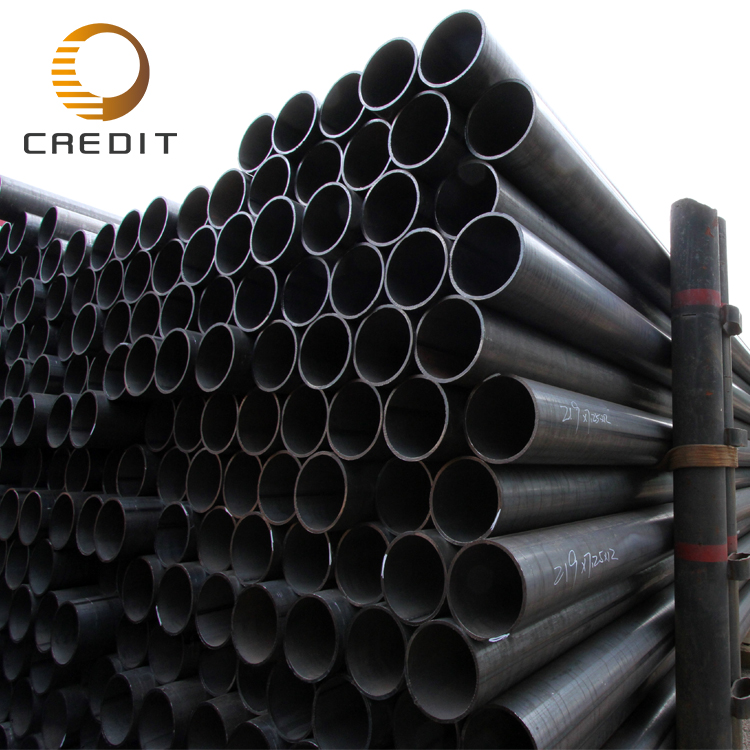

Quality assurance in welded pipe production involves stringent processes, including raw material inspection, real-time weld monitoring, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic and X-ray examination, and hydrostatic pressure testing. These measures ensure that the pipes meet required specifications and perform reliably in their intended applications, maintaining the industry's commitment to safety and excellence.